Impingement
- Diagnosis
- Non-operative Options
- Operative Options
- Before Your Surgery
- After Your Surgery
- Your Rehab
What is Shoulder Impingement?
Shoulder impingement is the condition of inflammation of the tendons of the shoulder joint. It is one of the most common causes of pain in the adult shoulder. The shoulder is a 'ball-and-socket' joint. A ‘ball' at the top of the upper arm bone, humerus, fits neatly into a 'socket’, called the glenoid, which is part of the shoulder blade or scapula. Shoulder impingement is also called as swimmer’s shoulder, tennis shoulder, or rotator cuff tendinitis.
Causes of Shoulder Impingement
Impingement results from pressure on the rotator cuff from part of the shoulder blade (scapula) as the arm is lifted. It is more likely to occur in young and middle-aged people who engage in physical activities that require repeated overhead arm movements. The pain may be due to a "bursitis" or inflammation of the bursa overlying the rotator cuff or a "tendonitis" of the cuff itself. In some circumstances, a partial tear of the rotator cuff may cause impingement pain.
Symptoms of Shoulder Impingement
Individuals with shoulder impingement may experience severe pain at rest and during activities, weakness of the arm and difficulty in raising the hand overhead.
Diagnosis of Shoulder Impingement
Diagnosis involves physical examination by the doctor where in the doctor checks for the possible range of movements with the affected shoulder. X-rays and MRI scans may be ordered to see the injury and inflammation.
- Physical Therapy Intro
- Shoulder and Elbow Steroid Injection
Conservative Treatment Options for Shoulder Impingement
Shoulder impingement can be treated with rest, ice packs, anti-inflammatory drugs, and avoiding activities involving the shoulder. Physical therapy may be advised to strengthen the muscles and steroid injections may be given if pain persists.
Want to know more?
Surgery for Shoulder Impingement
Arthroscopic surgery is recommended if the rotator cuff tendons are torn and to remove the bony spurs.

Once you and your doctor decide that surgery will help you, you will need to learn what to expect from the surgery and how to actively participate in the treatment plan for the best results afterward.
Preparing mentally and physically for surgery is an important step toward a successful result. Understanding the process, and your role in it, will help you recover more quickly and have fewer problems.
Before surgery, your doctor will perform a complete physical examination to make sure you don’t have any conditions that could interfere with the surgery or the outcomes.
- Routine tests, such as blood tests and X-rays may be performed.
- Discuss any medications you are taking with your doctor as you may have to stop or alter your intake before surgery. If you are taking aspirin or anti-inflammatory medications or any drugs that increase the risk of bleeding, you will need to stop taking them one week before surgery to minimize bleeding.
- Discuss with your doctor about preparing for potential blood replacement, medical interventions and other treatments prior to surgery.
- Report any infections to your surgeon. Surgery cannot be performed until all infections have cleared up.
- If you smoke, you should stop or cut down as smoking interferes with wound healing and can affect your recovery.
- Have someone available to take you home, as driving is not recommended for at least 24 hours or as advised.
- You may need help with everyday tasks such as cooking, shopping and laundry.
- Put items that you use often within easy reach, so you won’t have to stretch and bend as often.
- After Surgery Video
- Shoulder Surgery Recovery Video
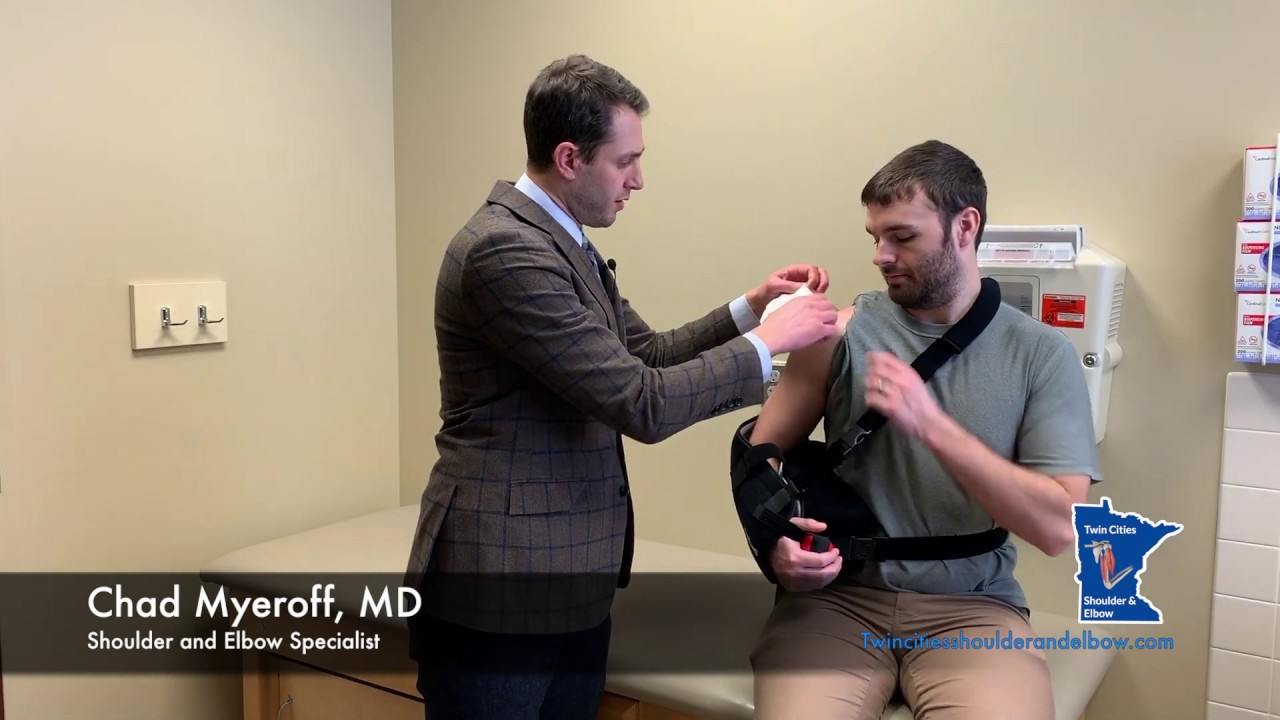
After the surgery, pain medications and antibiotics are prescribed to control pain and prevent infection. Your arm may be secured in a sling or cast.
Want to know more?
- Physical Therapy Intro Video
- Finger ROM Video
- Standard Elbow ROM Video
- Shoulder ROM Video
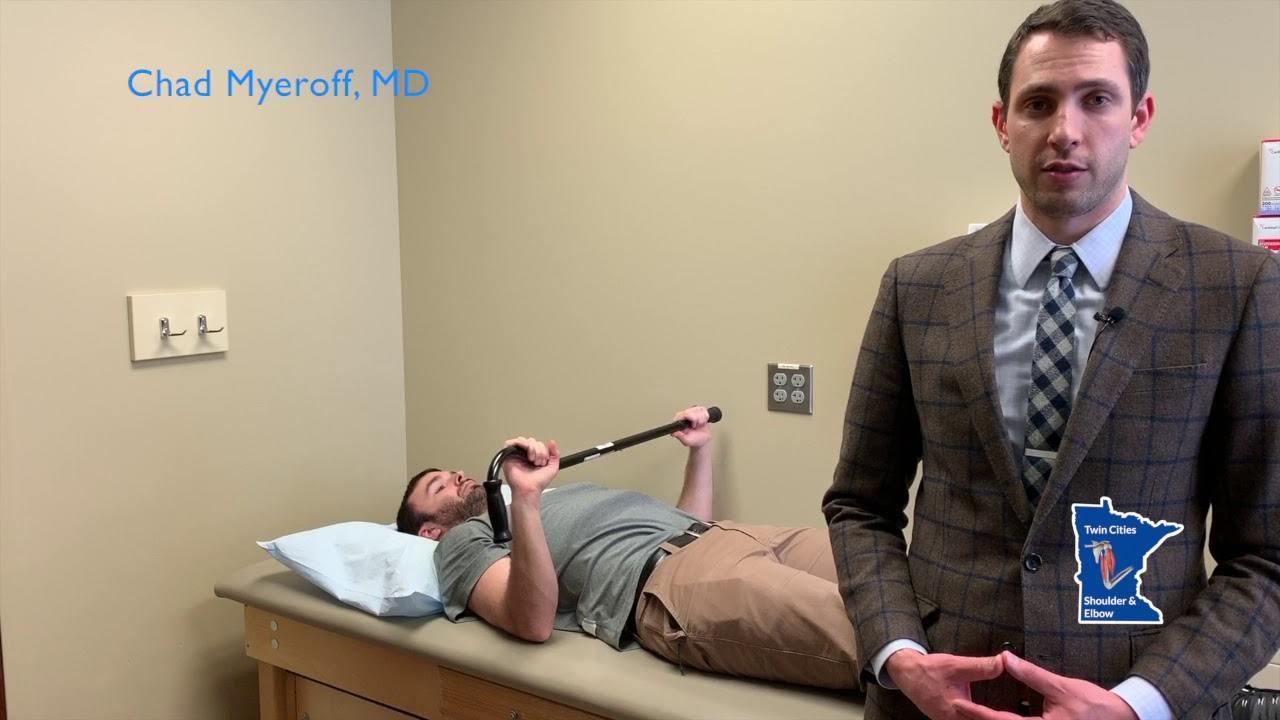
The rehabilitation program includes physical therapy, which is started soon after the surgery and is very important to strengthen and provide mobility to the shoulder. You may be able to perform gentle daily activities two to six weeks after surgery.
Want to know more?
- Download Dr. Myeroff's Shoulder Stretches Information Sheet
- Download Dr. Myeroff's Standard Elbow ROM Diagram Information Sheet
- Download Dr. Myeroff's Finger ROM Diagram Information Sheet
- Download Dr Myeroff's Post-Op Protocol for Arthroscopic Debridement and/or Subacromial Decompression
- Download Dr. Myeroff's Rotator Cuff Tear Non-Operative